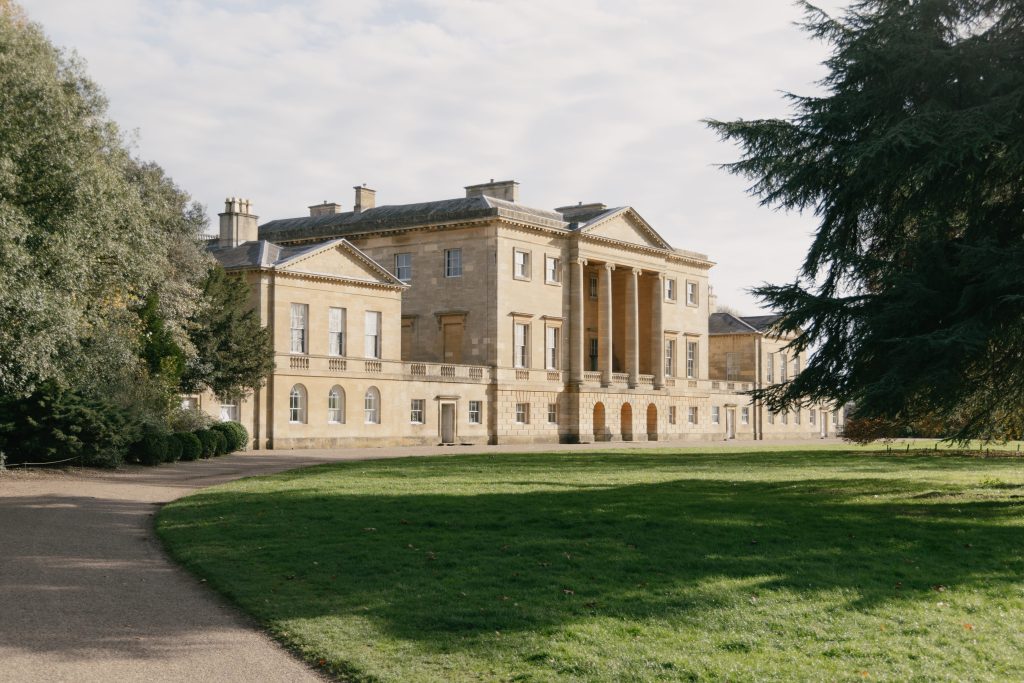
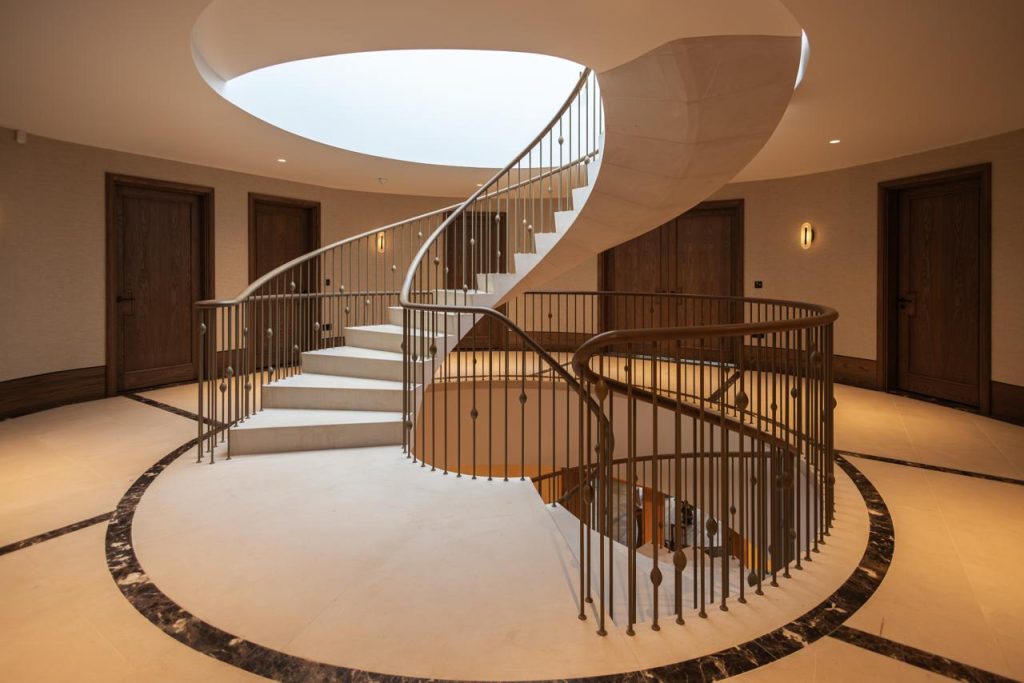
Architectural stonemasonry is a specialised field within the broader discipline of stonemasonry that focuses on the creation, preservation, and restoration of stone structures and sculptures. This field combines the technical skills of masonry with the artistic sensibilities of sculpture, resulting in works of functional beauty that can stand the test of time.
Stonemasonry itself is one of the oldest trades in human history, with evidence of man-made stone structures dating back thousands of years. Architectural stonemasonry, however, is a more recent development, emerging as a distinct discipline during the Renaissance period. Today, architectural stonemasons are responsible for creating and maintaining some of the world’s most iconic buildings and monuments.
History of Architectural Stonemasonry
The history of architectural stonemasonry is intertwined with the history of architecture itself. The earliest examples of architectural stonemasonry can be found in the ancient civilisations of Egypt, Greece, and Rome, where stone was used to construct a variety of structures, from temples and palaces to bridges and aqueducts.
During the Middle Ages, architectural stonemasonry was primarily used in the construction of cathedrals and castles. The Gothic style of architecture, in particular, showcased the skills of stonemasons with its intricate stone carvings and soaring arches. The Renaissance period saw a revival of interest in classical architecture and a renewed appreciation for the art of stonemasonry.
The Renaissance and Architectural Stonemasonry
The Renaissance period marked a significant turning point in the history of architectural stonemasonry. During this time, there was a renewed interest in the classical architecture of ancient Greece and Rome. This led to a revival of stonemasonry techniques that had been largely forgotten during the Middle Ages.
Architects and stonemasons began to study the works of the ancient masters, seeking to replicate their techniques and styles. This led to the creation of some of the most iconic buildings of the Renaissance period, including St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome and the Duomo in Florence.
Modern Architectural Stonemasonry
In the modern era, architectural stonemasonry continues to play a vital role in the construction and preservation of buildings and monuments. While modern technology has introduced new materials and construction methods, the basic principles of architectural stonemasonry remain the same.
Today’s architectural stonemasons use a combination of traditional hand tools and modern machinery to shape and fit stones. They also use a variety of techniques, including carving, chiseling, and polishing, to create intricate designs and finishes.
Principles of Architectural Stonemasonry
Architectural stonemasonry is guided by a set of fundamental principles that govern how stones are selected, shaped, and assembled. These principles are based on centuries of accumulated knowledge and experience, and they ensure that the finished work is both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound.
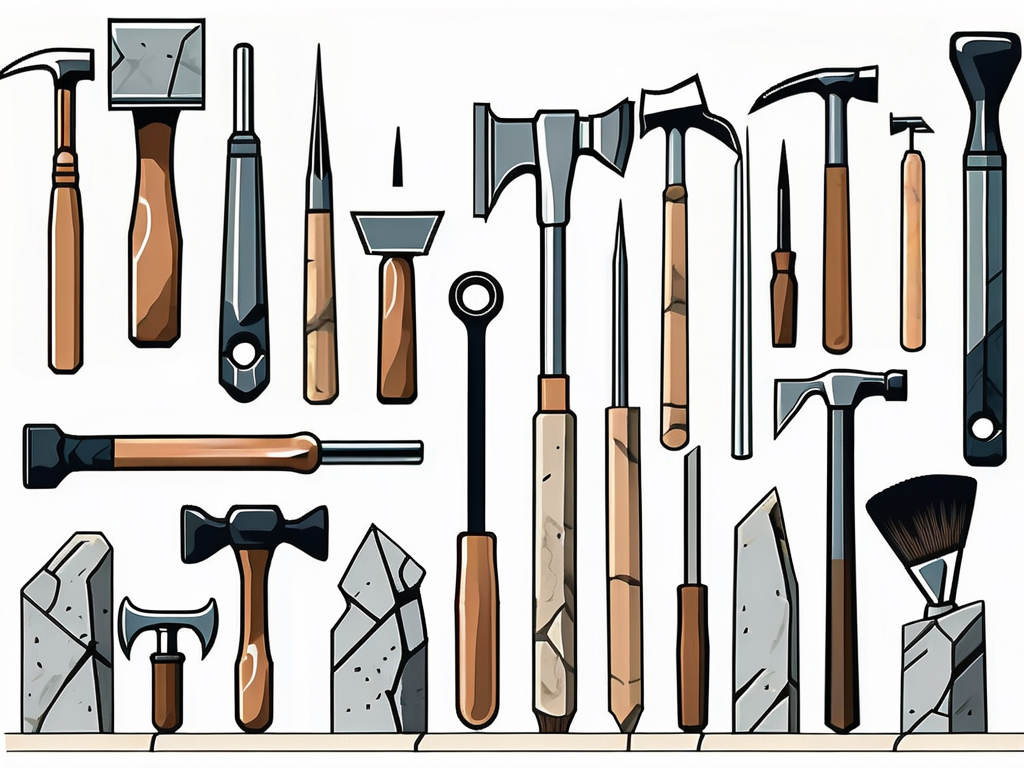

The first principle of architectural stonemasonry is the selection of the right stone for the job. Different types of stone have different properties, and the choice of stone can greatly affect the appearance and durability of the finished work. Factors to consider when selecting a stone include its color, texture, and hardness, as well as its resistance to weathering and erosion.
Shaping and Fitting Stones
The second principle of architectural stonemasonry is the shaping and fitting of stones. This involves cutting and shaping each stone so that it fits perfectly with the surrounding stones. The goal is to create a tight fit with minimal gaps, which helps to ensure the stability of the structure.
Shaping and fitting stones is a skill that requires both technical knowledge and artistic sensibility. The stonemason must understand the properties of the stone and how it responds to different tools and techniques. At the same time, they must have a keen eye for detail and a sense of aesthetics to ensure that the finished work is visually appealing.
Assembly and Construction
The third principle of architectural stonemasonry is the assembly and construction of the stone structure. This involves arranging the shaped stones in a specific order and securing them in place with mortar or other bonding materials. The process of assembly and construction requires careful planning and precise execution to ensure that the structure is stable and durable.
The assembly and construction process also involves the use of various techniques to enhance the appearance of the finished work. These techniques include the application of finishes and treatments to the stone, as well as the incorporation of decorative elements such as carvings and inscriptions.
Tools and Techniques in Architectural Stonemasonry
Architectural stonemasonry involves the use of a wide range of tools and techniques. These tools and techniques have evolved over time, but many of the traditional methods are still in use today.
The basic tools of the stonemason include hammers, chisels, and saws. These tools are used to cut and shape the stone, and they come in a variety of sizes and shapes to accommodate different types of stone and different tasks. In addition to these basic tools, stonemasons also use a variety of specialised tools, such as drills, grinders, and polishing machines.
Carving and Sculpting Techniques
One of the most important techniques in architectural stonemasonry is carving. Carving involves the removal of material from a stone to create a specific shape or design. This can be done using a variety of tools, including chisels, gouges, and rasps. The process of carving requires a high degree of skill and precision, as any mistakes can be difficult to correct.
Sculpting is a more complex technique that involves the creation of three-dimensional forms from stone. This requires a deep understanding of the properties of the stone, as well as a high level of artistic skill. Sculpting can be used to create a wide range of forms, from simple geometric shapes to complex figurative sculptures.
Finishing Techniques
Once the stone has been shaped and assembled, it is often treated with various finishes to enhance its appearance and protect it from the elements. These finishes can include polishing, which gives the stone a smooth, glossy surface; honing, which creates a matte finish; and flaming, which gives the stone a rough, textured surface.
Other finishing techniques include the application of sealants and protective coatings, which can help to prevent staining and weathering. These finishes can also be used to enhance the natural color and texture of the stone, adding depth and richness to the finished work.
Applications of Architectural Stonemasonry
Architectural stonemasonry has a wide range of applications, from the construction of buildings and monuments to the creation of decorative elements and sculptures. The versatility of stone and the skill of the stonemason allow for a wide range of styles and designs, from the traditional to the contemporary.
One of the most common applications of architectural stonemasonry is in the construction of buildings. Stone is a durable and versatile material that can be used in a variety of architectural styles, from the classical to the modern. It can be used for both structural and decorative elements, and it can be shaped and finished in a variety of ways to achieve different effects.
Monuments and Memorials
Architectural stonemasonry is also commonly used in the creation of monuments and memorials. These structures are often large and complex, requiring a high degree of skill and precision to construct. They are also often highly symbolic, with the design and materials chosen to convey a specific message or sentiment.
Monuments and memorials can range from simple stone markers to elaborate structures with intricate carvings and inscriptions. They can be found in a variety of settings, from cemeteries and parks to city squares and government buildings.
Decorative Elements and Sculptures
Another important application of architectural stonemasonry is in the creation of decorative elements and sculptures. These can be standalone pieces, or they can be incorporated into larger structures. They can be purely decorative, or they can serve a functional purpose, such as a fountain or a bench.
Decorative elements and sculptures can be created in a wide range of styles and designs, from the traditional to the contemporary. They can be carved from a single piece of stone, or they can be assembled from multiple pieces. They can also be finished in a variety of ways to achieve different effects.
The Future of Architectural Stonemasonry
Despite the advent of modern construction methods and materials, architectural stonemasonry continues to be a vital and respected trade. The skills and techniques of the stonemason are still in high demand, and the beauty and durability of stone continue to make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
As we look to the future, it is likely that architectural stonemasonry will continue to evolve and adapt. New technologies, such as computer-aided design and 3D printing, are already being used to enhance the precision and efficiency of the stonemasonry process. At the same time, there is a growing appreciation for the traditional skills and techniques of the stonemason, and a renewed interest in preserving and restoring historic stone structures.
Technological Advances
One of the most significant developments in architectural stonemasonry in recent years has been the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) technology. CAD allows stonemasons to create detailed digital models of their designs, which can then be used to guide the cutting and shaping of the stone. This not only increases the precision and accuracy of the work, but also allows for more complex and intricate designs.
Another promising development is the use of 3D printing technology. While still in its early stages, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionise the stonemasonry process by allowing for the creation of complex, three-dimensional forms from digital models. This could open up new possibilities for design and creativity in the field of architectural stonemasonry.
Preservation and Restoration
Another important aspect of the future of architectural stonemasonry is the preservation and restoration of historic stone structures. As these structures age, they require ongoing maintenance and repair to preserve their integrity and beauty. This work often requires the skills and expertise of a trained stonemason, who can replicate the original techniques and materials used in the construction of the structure.
Preservation and restoration work not only helps to preserve our architectural heritage, but also provides valuable training opportunities for stonemasons. By working on historic structures, stonemasons can learn and preserve traditional techniques that might otherwise be lost. This not only enriches the field of architectural stonemasonry, but also ensures that these skills and techniques will be passed on to future generations.
Discover the Art of Stone with AF Jones Stonemasons
Embrace the enduring legacy of architectural stonemasonry with AF Jones Stonemasons, where tradition meets innovation. With over 160 years of expertise, our team is dedicated to bringing your stone projects to life, from grand designs to intricate restorations. Whether you’re looking to preserve historical beauty or create a new masterpiece, we offer comprehensive services tailored to your needs. Visit our showroom in Oxfordshire, or make an enquiry today to see how we can support your vision and ensure that the art of stonemasonry continues to enhance our world for generations to come.