Bas-Relief: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
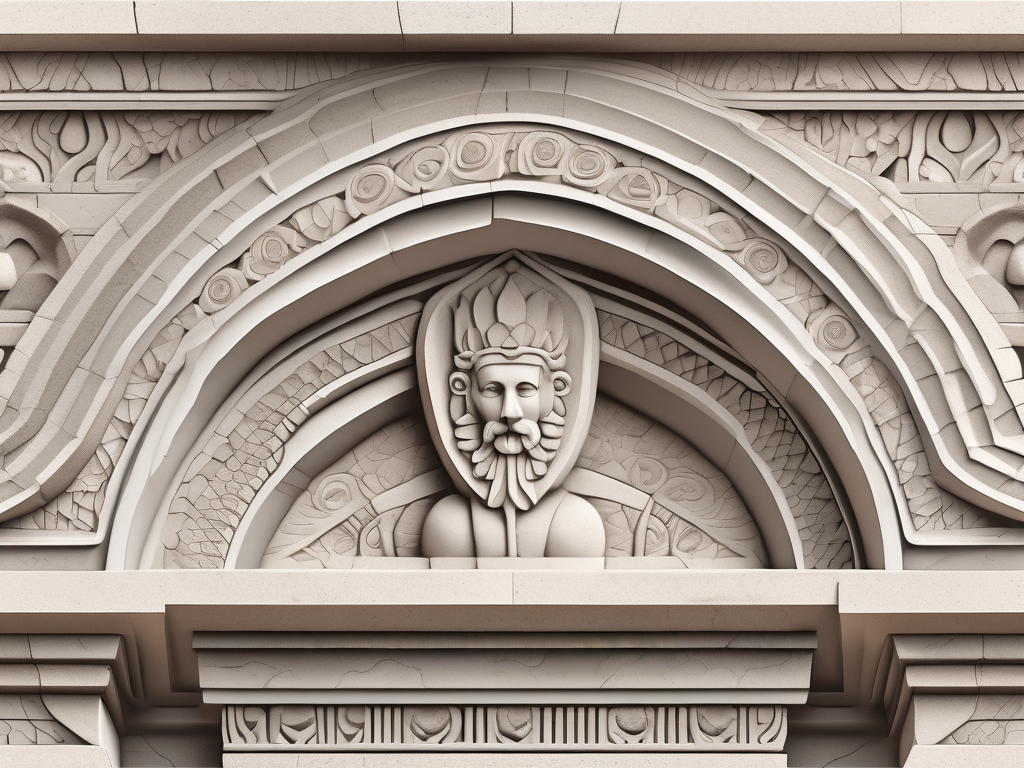

Bas-Relief, a term derived from the Italian words ‘basso’, meaning low, and ‘rilievo’, meaning relief, is a technique used in the field of architectural stonemasonry. This technique involves carving or etching images or designs onto a flat surface, such that they appear to be slightly raised above the background. The art of Bas-Relief has been […]
Column: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
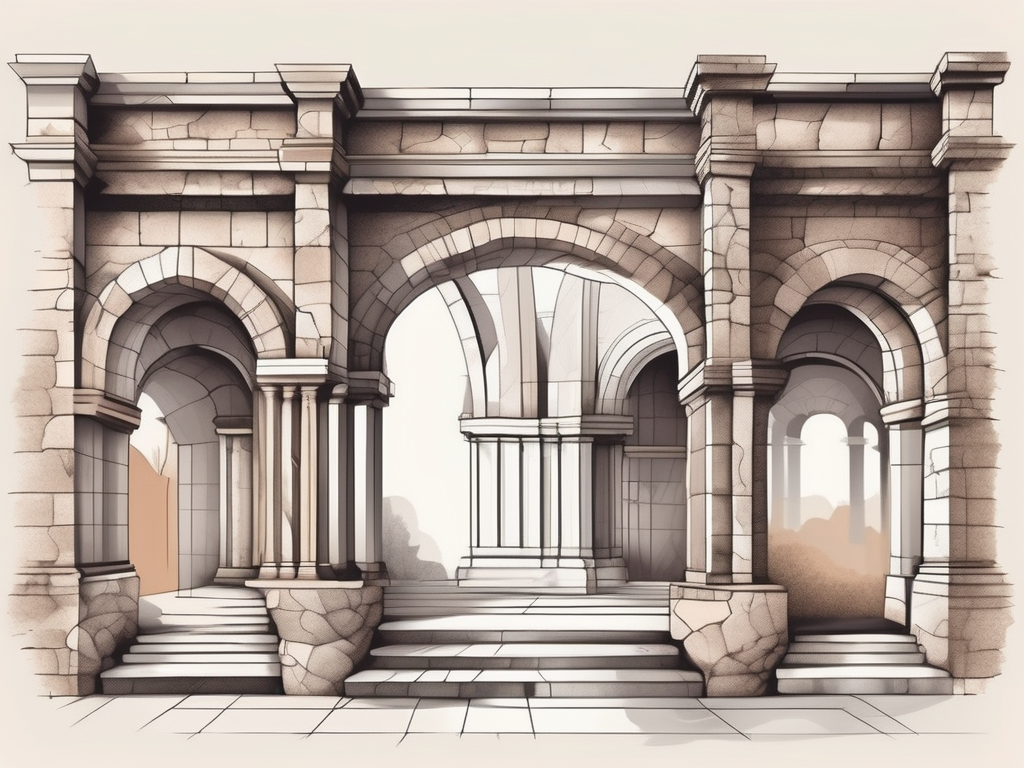

In the realm of architectural stonemasonry, the term ‘column’ holds significant importance. A column, in the context of architecture, is a vertical structural element that transmits the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a critical component in the support system of a building, bridge, or […]
Cornice: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
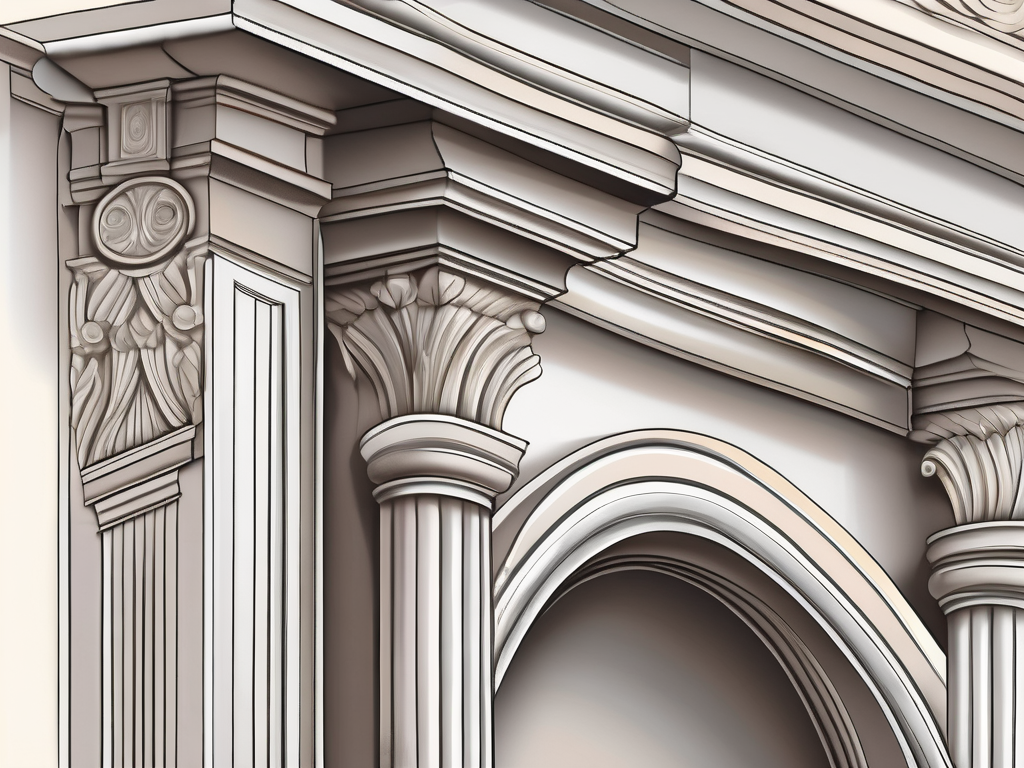

The term ‘cornice’ is derived from the Italian word ‘cornice’, which translates to ‘ledge’. In the realm of architectural stonemasonry, a cornice is a decorative moulding that crowns or completes buildings or furniture. This horizontal architectural feature is significant in the design and aesthetics of a structure, serving both functional and decorative purposes. While the […]
Facade: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
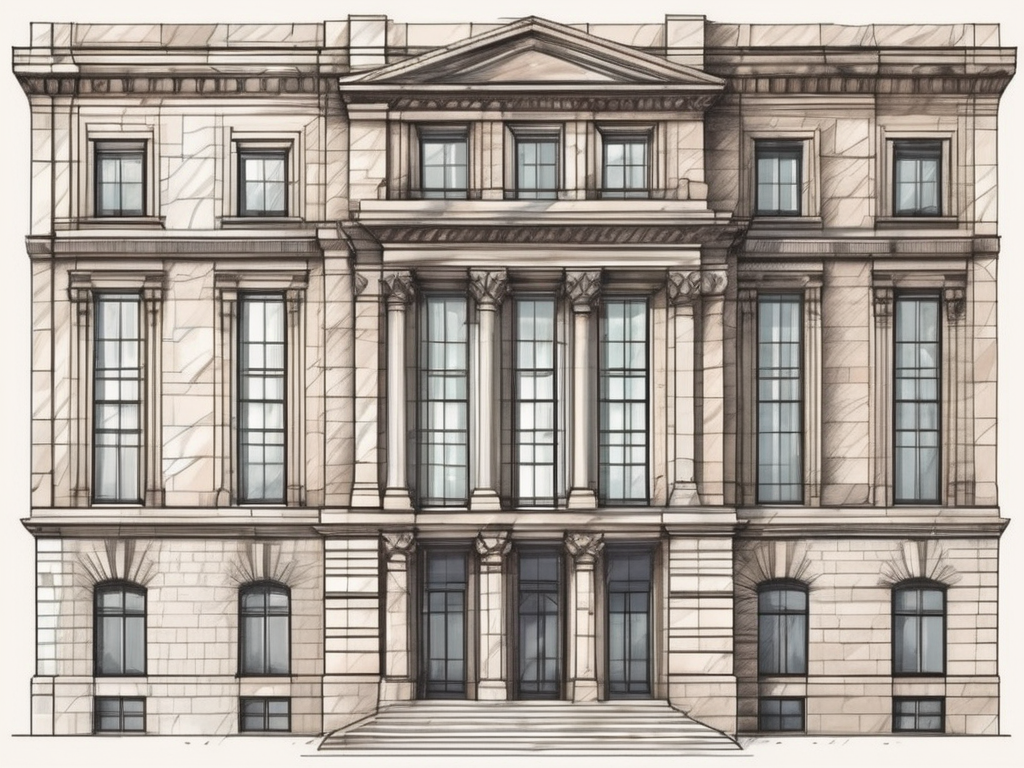

The term ‘facade’ in architectural stonemasonry refers to the exterior face of a building, particularly the front face or any side of the building that has special architectural treatment. The facade is a critical element in defining the architectural style of a building and often the most visually striking aspect. It serves both functional and […]
Inlay: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
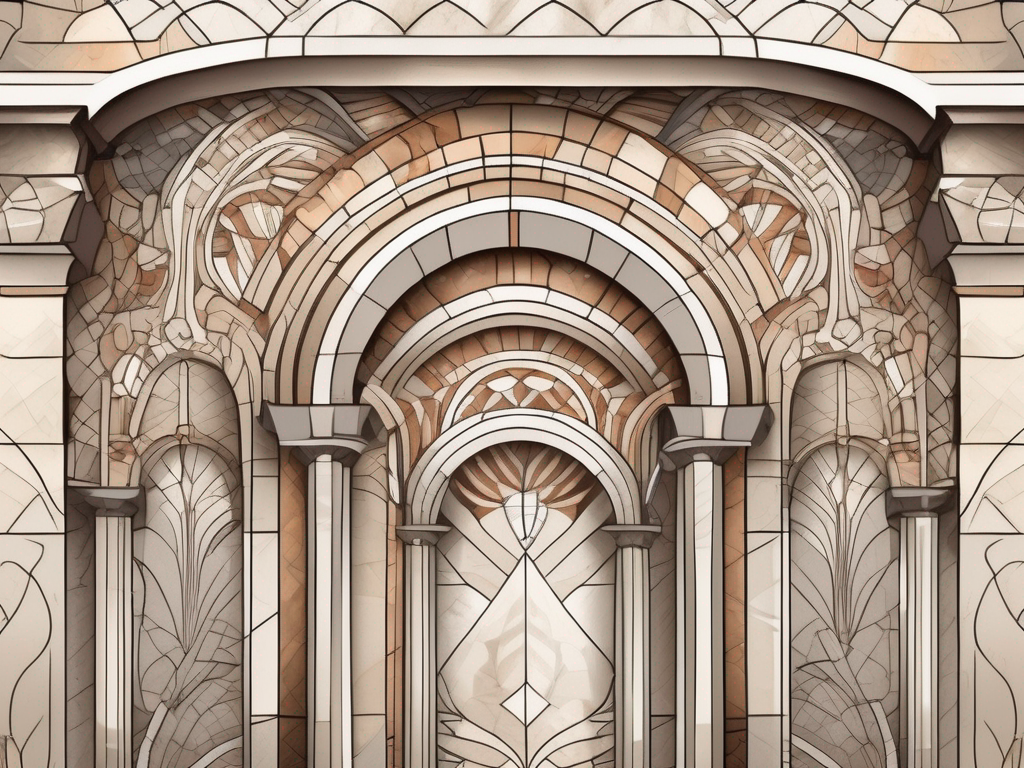

The term ‘Inlay’ in the context of architectural stonemasonry refers to a decorative technique where pieces of stone, marble, or other materials are embedded into a surface to create a design. This technique has been used for centuries in various architectural styles, providing a unique aesthetic appeal and a sense of depth and texture. In […]
Keystone: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained
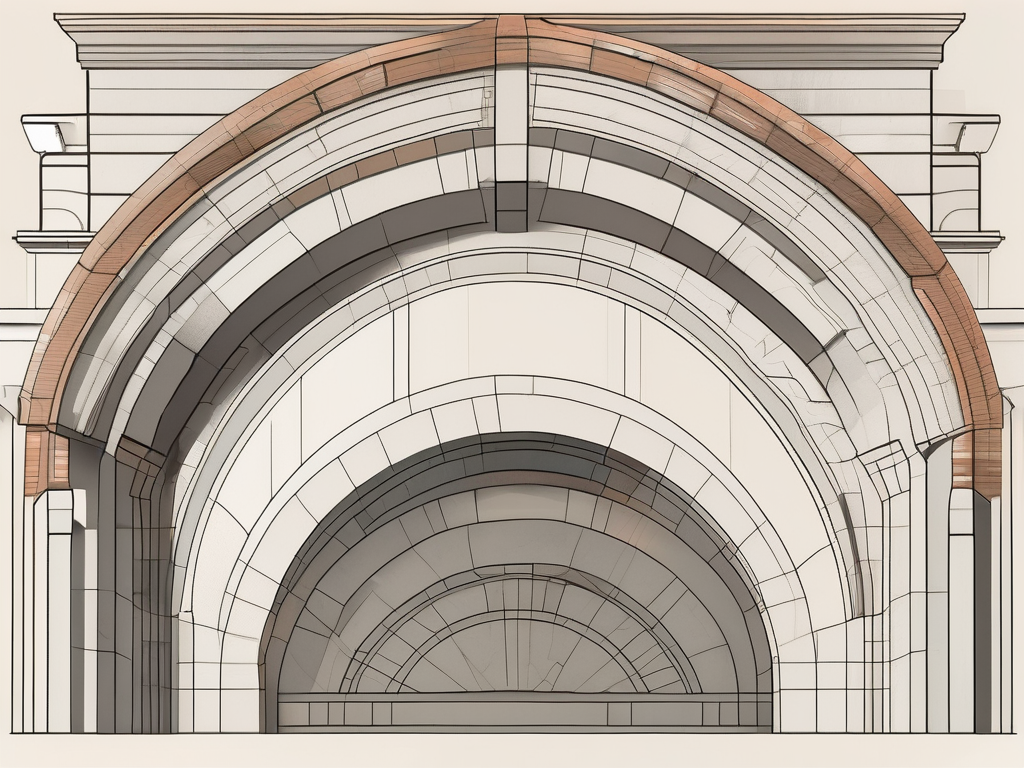
The keystone is a fundamental element in architectural stonemasonry, with its roots dating back to ancient times. This central stone, often found at the apex of an arch, serves not only as a structural component but also as a decorative feature, symbolising the strength and stability of the structure it supports. Keystones have been used […]
Masonry: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained

Architectural stonemasonry is a craft that dates back thousands of years and has been instrumental in the creation of some of the world’s most iconic structures. This ancient craft involves the shaping, arranging, and assembling of stone to create structures or monuments. It’s a craft that requires a deep understanding of the properties of stone, […]
Mortar: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained

Mortar, an integral component in architectural stonemasonry, is a workable paste used to bind building blocks such as stones, bricks, and concrete masonry units together, fill and seal the irregular gaps between them, and sometimes add decorative colours or patterns in masonry walls. In its broadest sense, mortar includes pitch, asphalt, and soft mud or […]
Pointing: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained

Pointing is a critical aspect of architectural stonemasonry, a craft that has been practiced for centuries and continues to be an essential part of modern construction. This process involves the finishing of mortar joints between stones or bricks in masonry construction. The term ‘pointing’ can also refer to the repair of existing joints that have […]
Quarry: Architectural Stonemasonry Explained

Quarrying is a process that involves the extraction of natural stone from the earth. This stone is then used in the construction of buildings, monuments, and other structures. The process of quarrying involves a series of steps, each of which is crucial to the overall success of the project. This article will delve into the […]